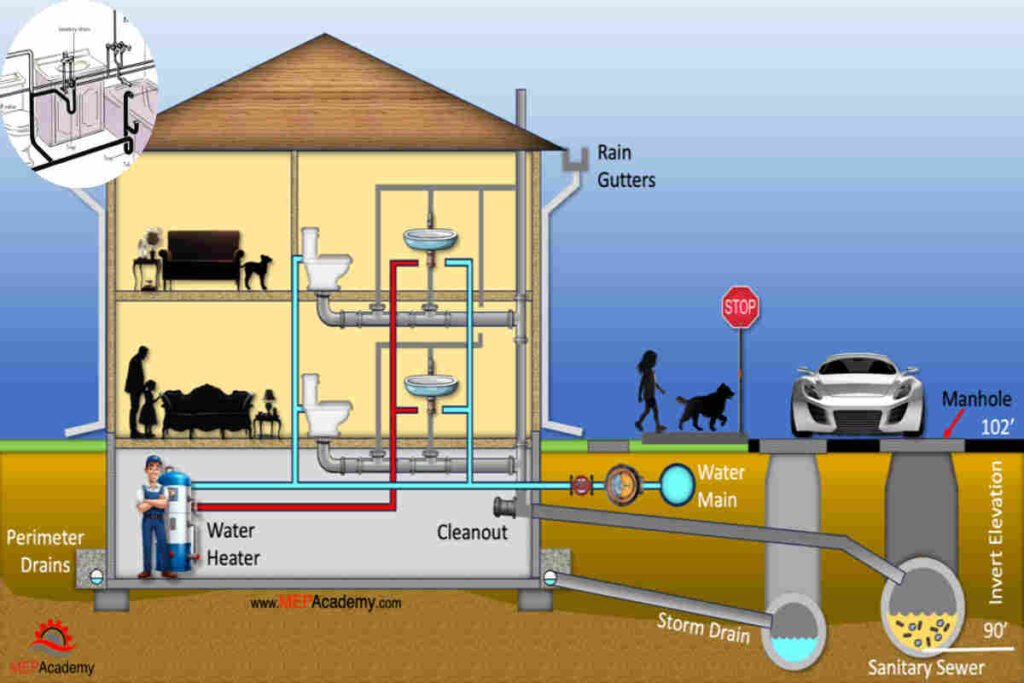
Understanding how to properly vent plumbing is crucial for every homeowner. Proper plumbing venting ensures your drainage system works effectively and prevents unpleasant odours from entering your living space.
What Is Plumbing Venting?
Definition and Purpose of Plumbing Vents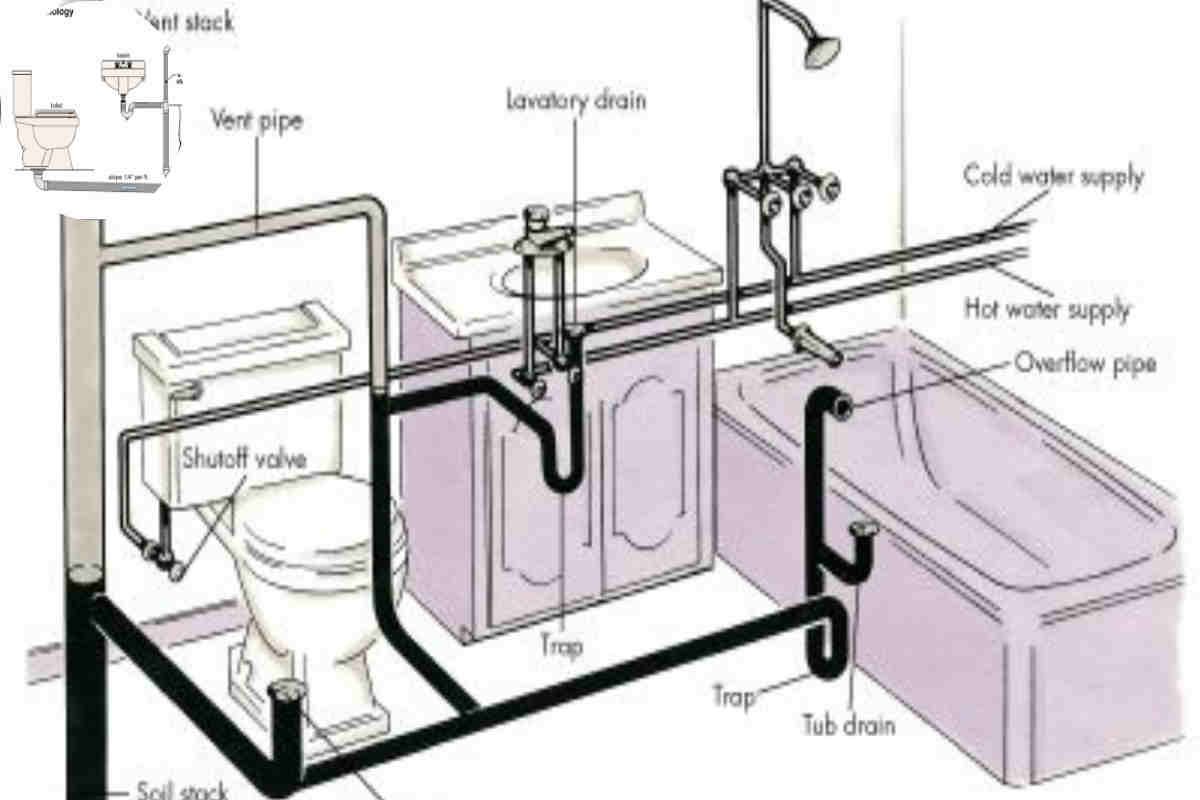
Plumbing venting refers to the system of pipes that allows air to enter the plumbing system. This movement of air is vital for maintaining necessary pressure levels, which helps smooth wastewater flow through the pipes. Without proper venting, the plumbing system can experience a variety of issues.
How Venting Impacts Drainage, Odour Control, and Fixture Performance
Venting plays a significant role in:
- Drainage: It prevents the creation of a vacuum in the drainage system, which can slow down or stop the water flow.
- Odour Control: It helps dissipate sewer gases, keeping your home odour-free.
- Fixture Performance: Proper venting ensures fixtures like sinks and toilets function optimally without backflow or slow drainage.
Common Misconceptions About Venting
Many homeowners believe that venting is only about preventing odours. However, ensuring efficient drainage and proper function of all plumbing fixtures is equally essential. Misunderstanding this can lead to improper installations and costly repairs.
Why Proper Venting Matters
Consequences of Improper Venting
Improper venting can lead to a myriad of issues, such as:
- Slow Drains: Without adequate air pressure, water cannot flow smoothly.
- Sewer Gas Accumulation: This can cause unpleasant odours and health hazards.
- Fixture Malfunctions: Toilets may gurgle, and sinks might not drain properly.
Benefits of Learning How to Properly Vent Plumbing
By understanding how to properly vent plumbing, both DIY enthusiasts and professionals can:
- Avoid Costly Repairs: Proper venting reduces the likelihood of plumbing malfunctions.
- Enhance Home Value: A well-vented plumbing system is an attractive feature for potential buyers.
- Improve Efficiency: Efficient plumbing can save water and reduce utility bills.
Understanding Plumbing Venting Codes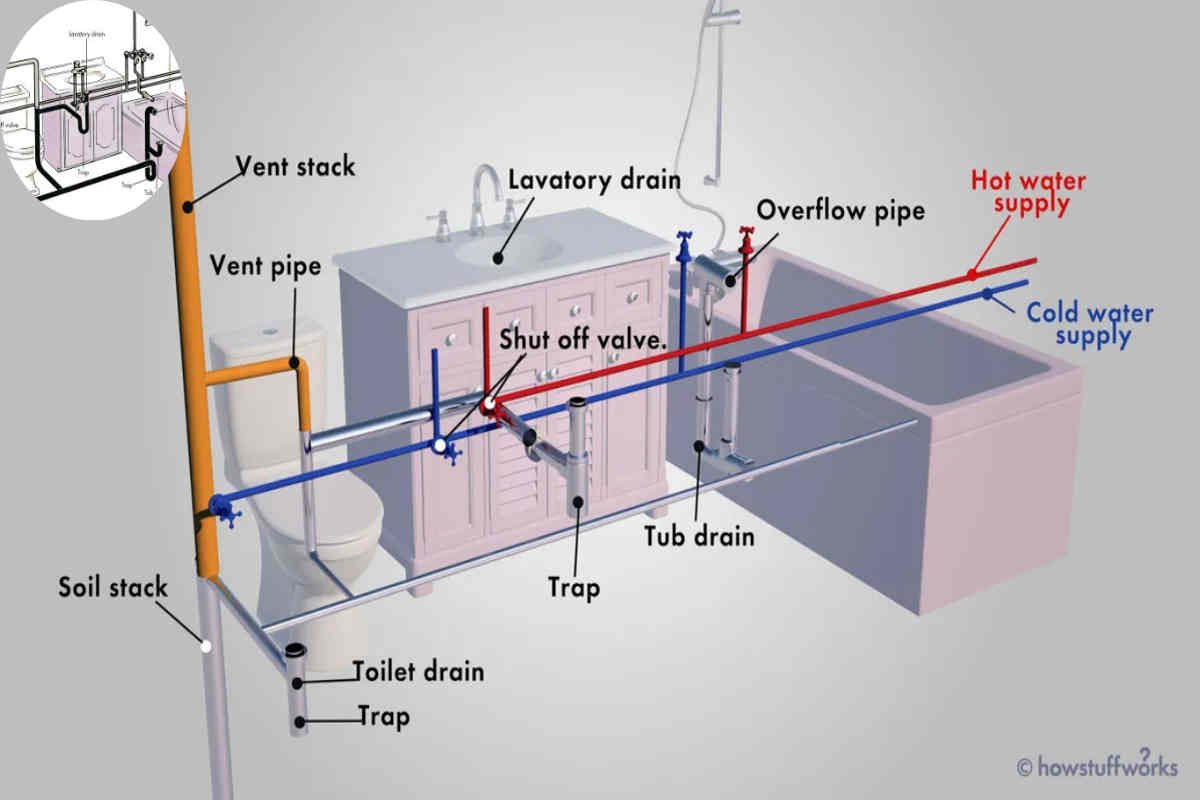
Importance of Following Local Plumbing Codes
Every region has specific plumbing codes designed to ensure safety and functionality. Following these codes is essential for avoiding legal issues and providing a safe living environment.
You may also read (white house plumbing)
Overview of National/International Code Requirements
While codes vary by location, standard requirements often include:
- Minimum pipe sizes for venting.
- Specific distances from the fixtures can be from the vent stacks.
- Adequate support and spacing for vent pipes.
How to Research Your Local Code Before Starting a Project
Before beginning any plumbing project, it is advisable to:
- Check Local Guidelines: Visit your local government or plumbing board’s website.
- Consult plumbing professionals: Seek advice from licensed plumbers who are familiar with local codes.
Key Components of a Plumbing Vent System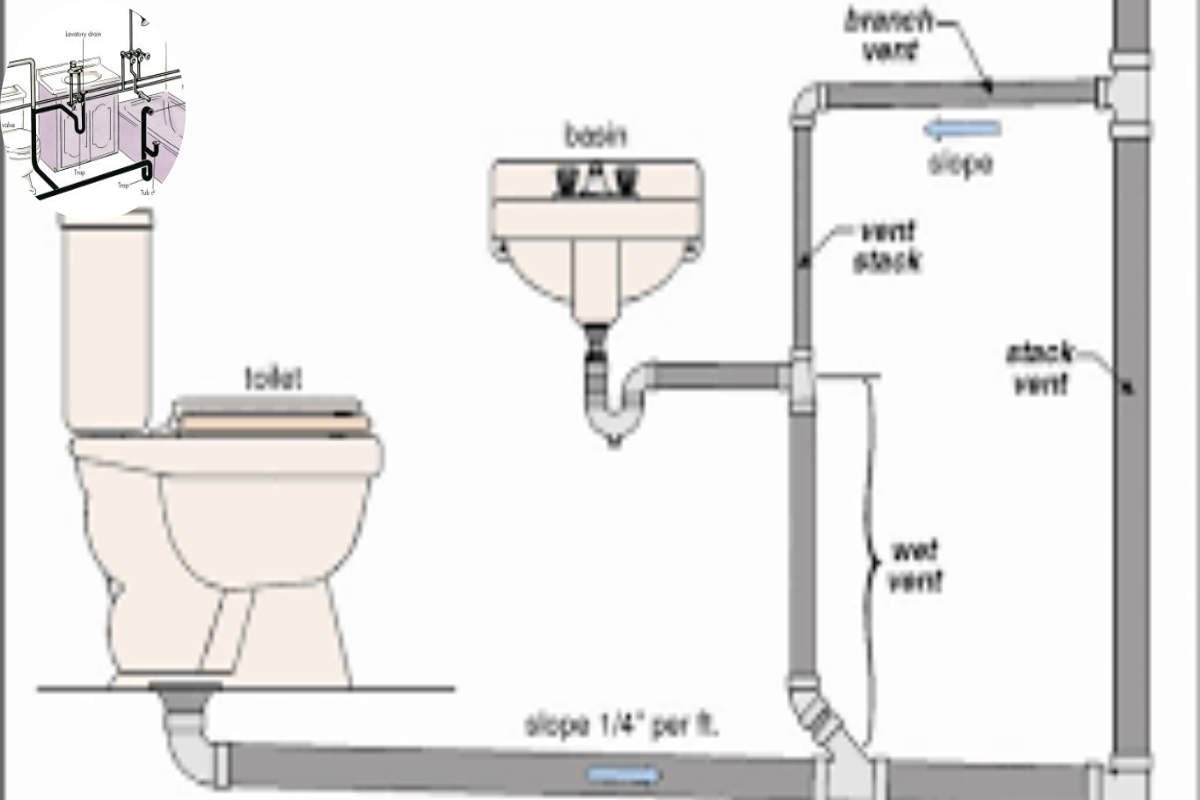
Understanding the components of a plumbing vent system is crucial for effective installation.
Main Vent/Vent Stack
The central vent, or vent stack, is the vertical pipe extending from the plumbing system to the roof. It allows air to enter the system and facilitates the escape of gases.
Branch Vents
Branch vents are smaller pipes that connect individual fixtures to the central vent. They help to ensure that each fixture has adequate venting.
Air Admittance Valves (AAVS)
Air admittance valves are mechanical devices that allow air to enter the plumbing system without letting sewer gases escape. They are instrumental in situations where traditional venting is not possible.
Cleanouts and Access Points
Cleanouts are access points in the plumbing system that allow for easy cleaning and maintenance. They should be strategically placed throughout the venting system.
Types of Plumbing Venting Methods
Individual (Conventional) Venting
Individual venting is used for single fixtures, allowing them to vent directly to the main stack. This method is simple and effective for straightforward installations.
Common Venting
Standard venting serves multiple fixtures, connecting them to a single vent stack. This method is efficient for bathroom or kitchen layouts with closely positioned fixtures.
Wet Venting
Wet venting combines the drain and vent functions, allowing a single pipe to handle both. This technique is commonly used in bathroom layouts where space is limited.
Circuit Venting
Circuit venting is designed for a group of fixtures, allowing them to share a vent. This method is particularly effective in multi-fixture bathrooms.
Island Fixture Venting
Island fixture venting is a unique technique used for kitchen islands. Since these fixtures are detached from walls, special venting methods, such as AAVS, are necessary.
Relief Vents
Relief vents are essential in multi-story buildings to prevent pressure buildup and ensure proper floor drainage.
Combination Waste and Vent Systems
This system combines waste and venting functions into a single pipe. It is an efficient solution for specific plumbing configurations.
Step-by-Step: How to Properly Vent Plumbing
Plan Your Venting Layout
Mapping out your fixtures and drain lines is crucial. Determine vent locations for each fixture to ensure optimal performance.
Select the Right Venting Method
Choose the venting type that best matches your fixtures and layout. Each method has advantages and should be selected based on specific needs.
Sizing and Slope
Proper sizing of vent pipes is critical. Follow local codes for pipe diameters and maintain the required slopes to prevent blockages.
Installation Best Practices
- Cutting and Joining Pipes: Use proper tools and techniques to ensure secure connections.
- Routing: Carefully route pipes through walls, ceilings, and roofs while adhering to building codes.
- Connecting: Ensure proper connections to the main vent stack or utilise AAVS where allowed.
Special Situations
- Venting in Remodels: Use AAVS and horizontal vents in tight spaces.
- Island Sink Venting: Follow specific steps to vent island sinks effectively.
- Multi-story Venting Tips: Implement relief vents and offsets to accommodate vertical plumbing needs.
Testing Your Vent System
Once installed, check for proper airflow and drainage. Regularly inspect for leaks and ensure compliance with local codes.
Troubleshooting Common Venting Problems
Signs of Venting Issues
Common indicators of venting problems include:
- Gurgling Sounds: This can signal air blockage.
- Slow Drains: A sign of inadequate air pressure.
- Sewer Smell: Indicates gas leaks or vent issues.
Simple Diagnostic Steps
- Inspect Vent Pipes: Check for blockages or kinks.
- Check Fixtures: Ensure all fixtures are draining properly.
- Assess AAVS: Ensure they are functioning correctly.
When to Call a Professional Plumber
If you encounter persistent issues or are unsure about your venting system, it’s best to consult a professional plumber for assistance.
Maintenance Tips for Home Plumbing Vents
Regular Inspection Routines
Conduct regular checks on your plumbing vents. Look for any signs of damage or blockage.
Clearing Debris and Preventing Blockages
Keep vent openings clear of debris, especially during seasonal changes. Regular cleaning can prevent many issues.
Seasonal Considerations
Be mindful of seasonal impacts, such as:
- Winter Freezing: Insulate vent pipes to prevent freezing.
- Roof Vent Obstructions: Regularly clear snow or debris from roof vents.
You may also read (house plumbing business).